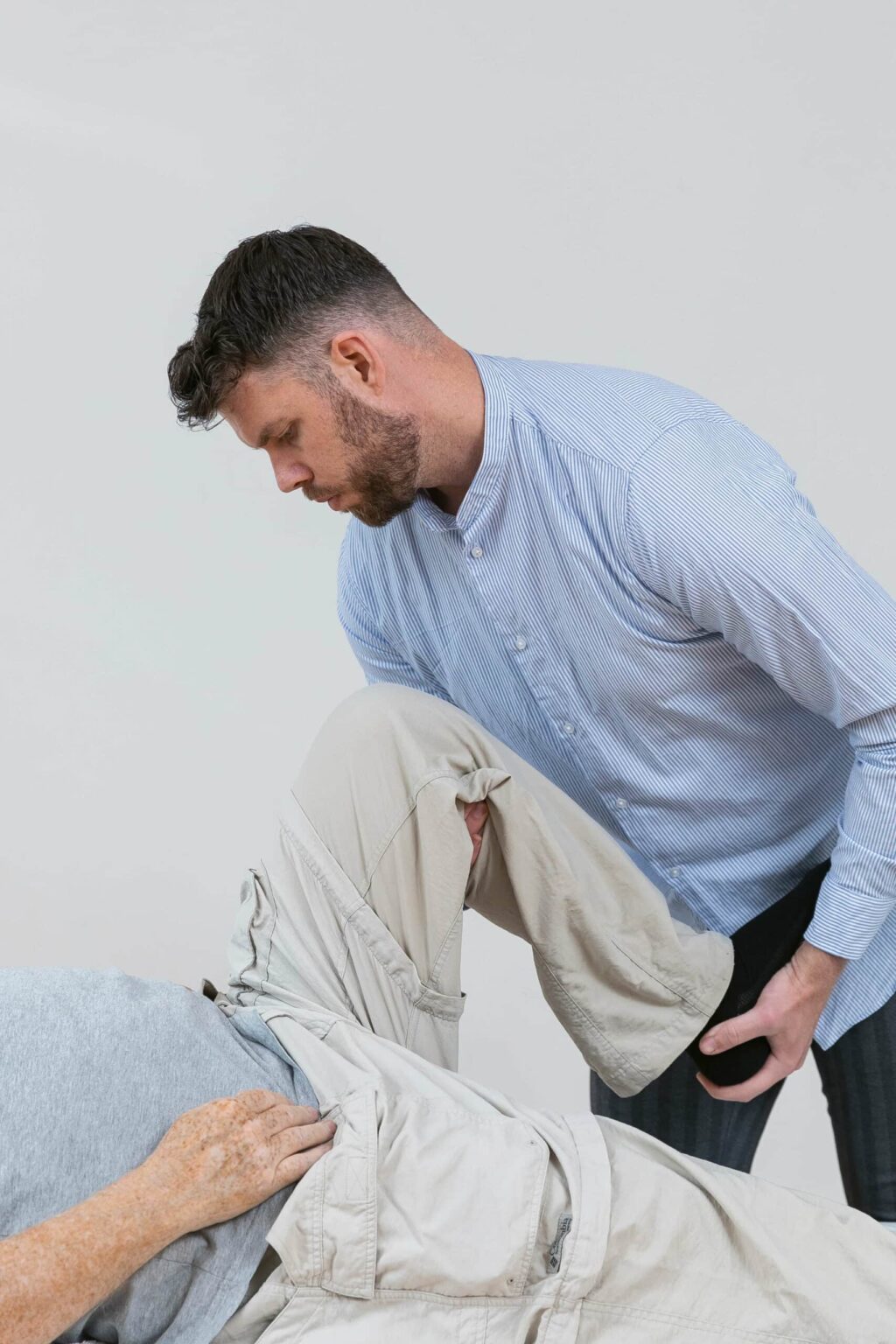
We treat
Sprains
Learn more about sprains and their treatment
What are sprains?
Sprains are something most of us have encountered at least once in our lives. But what exactly is it and how can osteopathy help? Let’s delve into the subject.
Jump to section [Show]
Causes of sprains
Imagine taking a wrong step or suddenly falling and feeling a pain in your wrist or ankle – this is typically the result of a sprain. A sprain is when there is damage to one or more ligaments and/or soft tissue around a joint.
Common causes of sprains can be:
- Sudden movements: Sharp or sudden movements, especially when the movements are made without proper preparation or warm-up, can lead to sprains. This can occur during sports, exercise, or even everyday activities.
- Fall or trip: An unexpected fall or tripping and landing in an unfortunate way can result in a sprain.
- Sports injuries: Activities such as running, ball games, or other sports that involve sudden movements, awkward landings, or collisions can increase the risk of sprains.
Source: Sundhed.dk

Symptoms of a sprain
Symptoms of a sprain can range from mild to severe, depending on the degree of ligament damage. Sprains can occur in virtually any part of the body, but are most common in the ankles and wrists.
Typical symptoms of a sprain include:
– Pain around the injured joint.
– Local swelling and tenderness.
– Bruising or discoloration of the skin in the area.
– Reduced mobility around the joint.
– The patient has a feeling of instability in the joint.
Fracture or sprain?
Once the injury has occurred, it can be difficult to distinguish between a sprain and a fracture. In both cases, symptoms can include pain, swelling, and decreased mobility. It is therefore important to get a correct diagnosis so that the right treatment can be initiated.
Fracture: This occurs when the bone is broken. A fracture can be complete, where the bone is broken into two pieces, or it can be a crack or tear in the bone. A fracture can be open, where the bone protrudes through the skin, or closed, where the bone is broken but the skin remains intact.
Sprain: This occurs when the ligaments that connect the bones in a joint are overstretched or damaged. This can cause pain, swelling, and decreased mobility in the affected area, but the bone is usually not broken.

How to distinguish between a fracture and a sprain
These features can help distinguish between a fracture and a sprain, but it is essential to get a professional evaluation. Healthcare professionals can use X-rays or other diagnostic methods to determine the extent and nature of the injury and guide appropriate treatment.
| Symptom | Fracture: | Sprain: |
|---|---|---|
| Pain: | Often intense pain, especially when touching or moving the affected area. | Pain, but often less intense than with a fracture. |
| Swelling: | Swelling may occur around the fractured area. | Swelling around the joint is common. |
| Discolouration: | Discolouration of the skin, such as bruising or redness, may occur. | Depending on the ligament damage, bruising or redness may also appear in various colour shades over time. |
| Deformity: | If the bone is broken in two, it can result in a visible deformity. | Reduced mobility in the injured area, but usually no visible deformity. |
What can I do myself about a sprain?
In the event of a sprain, you can take several steps to relieve symptoms and promote healing.
To avoid or reduce swelling immediately after the injury has occurred, you can use the RICE Method:
1. (R) Rest.
Avoid putting any additional stress on the injured area in the first phase. If necessary, use a splint or support bandage to stabilize the joint.
2. (I) Ice.
Apply ice to the affected area for short periods of time (about 15-20 minutes at a time) to reduce swelling and relieve pain. Always use a cloth or towel between the ice and the skin to prevent frostbite.
3. (C) Compression.
Apply compression using an elastic bandage or compression wrap to reduce swelling. Make sure it is not too tight as this can restrict circulation.
4. (E) Elevate.
Elevate the injured area above the level of your heart to reduce swelling. Use pillows or a rolled blanket to support elevation.
5. Exercises.
Once the swelling and pain have subsided, gentle exercises to restore mobility and strength may be beneficial, but this should be done in consultation with a healthcare professional.
Source: Regionsyddanmark.dk

Rehabilitation after sprain
Rehabilitation after a sprain is important to regain full range of motion, strength, and stability in the affected area. Both physiotherapy and osteopathy can play an important role in the rehabilitation process, but they have slightly different approaches.
Physiotherapy:
Physiotherapists specialize in the rehabilitation and retraining of musculoskeletal issues, including sprains. At Aarhus Osteopathy, our physiotherapists will develop a tailored exercise program that focuses on improving muscle strength, mobility and function.
Osteopathy:
Osteopaths also have expertise in musculoskeletal conditions, but the approach here will be more holistic. The focus is on improving the overall function of the body through the use of manual techniques together with advice on rehabilitation. As an osteopath, there will be a strong focus on minimizing and breaking down the compensations that one typically acquires after a sprain.
After an ankle sprain, for example, a number of biomechanical compensations can be triggered in the body:
- Altered gait: The person’s walking pattern may change to compensate for the pain in the ankle. This may include shifting weight, changing hip movement, or shrugging the shoulders.
- Overuse of other joints: To compensate for decreased function in the ankle, other joints, such as the knees, hips, and back, may become overused. This can increase the risk of further injury or overuse in these areas.
- Muscle imbalance: An ankle sprain can lead to an imbalance in the muscles around the ankle. Some muscles may become weaker while others become tighter, which can affect the stability and mobility of the joint.
Prevention of sprains
Sprains can be prevented by implementing some measures that reduce the risk of injury. In general, sprains can be prevented through:
Heating:
Do a proper warm-up before starting your activity. This helps increase blood circulation and prepare your joints and muscles.
Flexibility exercises:
Include regular stretching exercises to improve flexibility and mobility in muscles and joints.
Stability training:
Stability training can be an effective way to prevent sprains by strengthening the muscles around your joints and improving your overall body stability. This can improve your body control and responsiveness, especially if you participate in activities that carry a risk of injury.
Strength training:
Build muscle strength around your joints with targeted strength training exercises. Focus on strengthening specific muscle groups and improving the coordination between muscles and ligaments. This can reduce the risk of injury and improve stability.
Source: Danske Fysioterapeuter

Myths about sprains
Myths about sprains are widespread. Here are some of them:
| Myth | Fact |
|---|---|
| Sprains and strains are the same? | Sprains involve damage to ligaments, while strains concern injuries to muscles or tendons. They are different types of injuries. |
| If you can put weight on it, it’s not a serious sprain? | Some sprains may allow weight-bearing, but that doesn’t necessarily mean they are not serious. A professional assessment is important for an accurate diagnosis. |
| You can always feel it if you have a sprain? | Some sprains can be mild and may not cause intense pain. It is important to be aware of swelling and reduced mobility. |
| Swelling always happens immediately with a sprain? | Swelling can develop gradually over time, and it is not always immediately visible after a sprain. |
| Sprains can heal completely without consequences? | Although many sprains heal over time, some may lead to long-term effects or compensatory patterns. This can increase the risk of recurrent injuries. |
NOTE: It is important to have accurate information and avoid basing decisions about treatment and prevention on myths, and in case of doubt or serious injuries, it is always wise to consult a healthcare professional.
Nutrition and recovery after an injury
Maintaining a healthy, balanced diet rich in nutrients can support the healing process and contribute to more effective rehabilitation after sprains and other injuries. Protein and calcium, among others, play a crucial role in your healing process after injuries like sprains.
Protein, found in foods such as meat, fish, dairy products, legumes and nuts, is necessary for tissue repair and muscle building. It actively contributes to the rebuilding of damaged cells and promotes a faster healing process.
When it comes to sprains, calcium is just as important. Calcium is a key component in building bone tissue, and its presence is essential for bone healing. Foods like dairy products, nuts, seeds, and green leafy vegetables are good sources of calcium.
Together, protein and calcium form a powerful combination that strengthens the overall healing process of your tissues. Protein helps repair and rebuild damaged structures, while calcium is essential for maintaining bone strength.
By integrating these nutrients into the diet in general, but also after a sprain, you can positively influence tissue repair, contributing to a more efficient and complete recovery process after a sprain.

When should you see a doctor?
It can be challenging to assess the severity of the injury yourself. In less serious cases, it is not necessary to seek immediate medical attention – instead, you can start the RICE treatment on your own.
In more serious cases, where the function of the joint is impaired, or there is pain in the knee or ankle joint that prevents you from supporting your leg, you should seek medical attention or go to the emergency room. If your joint is significantly swollen or the joint is not sitting correctly after the injury, it is recommended to go to the emergency room, where X-rays may be necessary to rule out bone fractures.

Often related problems
Jaw joint pain

Vitamin deficiency – spot & control the symptoms

Trigger finger

Carpal tunnel syndrome

Sprains

Tenosynovitis

Nerve pain

