We treat
Running injuries
Learn more about running injuries on this subpage.
Running injuries
Many people run and some suffer a running injury every year, which means they cannot maintain the active lifestyle that increases quality of life and reduces the risk of lifestyle diseases.
Jump to section [Show]
Acute running injuries
This type of injury occurs suddenly – often as a blow, impact, fiber damage, sprain or similar. These injuries can occur by accident, but they can also occur due to dysfunctions or incorrect positions in the body that have increased the risk of injury.
What you can do for acute running injuries – RICEM
- R – Keep the injured area calm. (Rest)
- I – Put ice on the area. (Ice)
- C – Bandage the area and apply some compression. (Compression)
- E – Elevation of the area above heart level.
- M – Move as soon as you feel the injured area can withstand being mobilized. (Mobilization)
Running injuries from overuse
Overuse injuries occur when you exceed the tissue’s load capacity. These injuries often occur insidiously, over a long period of time, or when the load level increases suddenly.In overuse injuries, there is always one or more dysfunctions or misalignments that cause only the injured area to start making sound (pain)..
What can you do about overuse injuries
Reduce the load level until your body can handle “repairing” the damage.
If this doesn’t help, you may need to take a short break.
Make sure that your neck, chest, back, pelvis and legs are flexible enough. Get good, long sleep, reduce stress in your daily life and optimize your diet.
Chronic running injuries
You can consider your injury chronic if it has lasted for several months without improvement, or if the same injury always occurs as soon as you start running again. This is an indication that your body is unable to heal the area at all due to major dysfunctions in one or more of the systems that provide for your body’s healing.
What you can do for chronic running injuries
Make sure you get good, long sleep, reduce stress in your daily life, and optimize your diet. It is also important that you restructure your work if it consists of a lot of sedentary work.
Get up often, walk around a bit, or take breaks to stretch your legs.
This stimulates your circulatory system, which is essential for the body to heal from injuries. It is also important to optimize flexibility in the neck, chest, back, pelvis and legs.

Osteopathic approach to running injuries
We are experts in diagnosing and we are specialists in treating the causes of running injuries. We individually analyze the mobility of all areas that running requires. We can treat acute and chronic injuries and we also offer preventive treatment of running injuries.
First, the structure causing the pain must be determined. The cause of the injury must be found – often somewhere else in the body than the actual injured area. Weak mechanical areas must be examined in relation to the different body types.
All systems in the body; the musculoskeletal system, the blood system, the lymphatic system, the organ system and the craniosacral system must be examined in relation to the body’s ability to heal the current injury.
Osteopathy examines, regulates, stimulates and restores all systems and areas in the body that are not functioning optimally, so that the body is able to heal the running injury.
Running injuries often require physiotherapy rehabilitation to strengthen and stabilize muscles and connective tissue.
Body type and its importance for the development of running injuries
Every human being can be placed into three main groups:
The Ectomorph
The ectomorph, who is tall and slim – is particularly suitable for endurance sports, as the body type is good for rotations, among other things. This body type typically has fine bone structure, small shoulders and chest. The ectomorph has a high metabolism, which means that they can have great difficulty gaining weight. The ectomorph can often get injuries to the hip flexors, pelvis (e.g. pelvic joints), knee injuries (e.g. plica and meniscus injuries) and foot injuries (e.g. sunken forefoot).
The mesomorph
The mesomorph, who is muscular and athletic – especially suited to anaerobic work that requires great strength over a short period of time. Mesomorphs are strong, athletic, muscular and often hard body types with very well-shaped muscles. They have broad shoulders and dense bone structure that can easily build muscle and lose fat, but they may have a harder time losing weight than the ectomorph. The mesomorph will often experience injuries/pain on the outside and inside of the knees (e.g. runner’s knee and bursitis), hips (e.g. groin injuries, sciatica and overload of hip muscles) and ankles (e.g. overload of calf muscles).
The endomorph
The endomorph, who is more heavily built with large bones and a lower metabolism – best suited for heavy work. The endomorph is densely built, has shorter limbs and may have difficulty losing weight due to a low metabolism. The endomorph will often suffer from back pain, shin splints, inflammation in several places in the body (e.g. Achilles tendonitis and bursitis) and heel spurs under the foot.
These types all have strengths and weaknesses, which is why they each often get certain types of running injuries. Aarhus Osteopathy – osteopathy and physiotherapy look individually at the different body types, their weaknesses and limitations precisely to optimize the body’s ability to move during running.

Often related injuries

Side stitch

Padel injuries
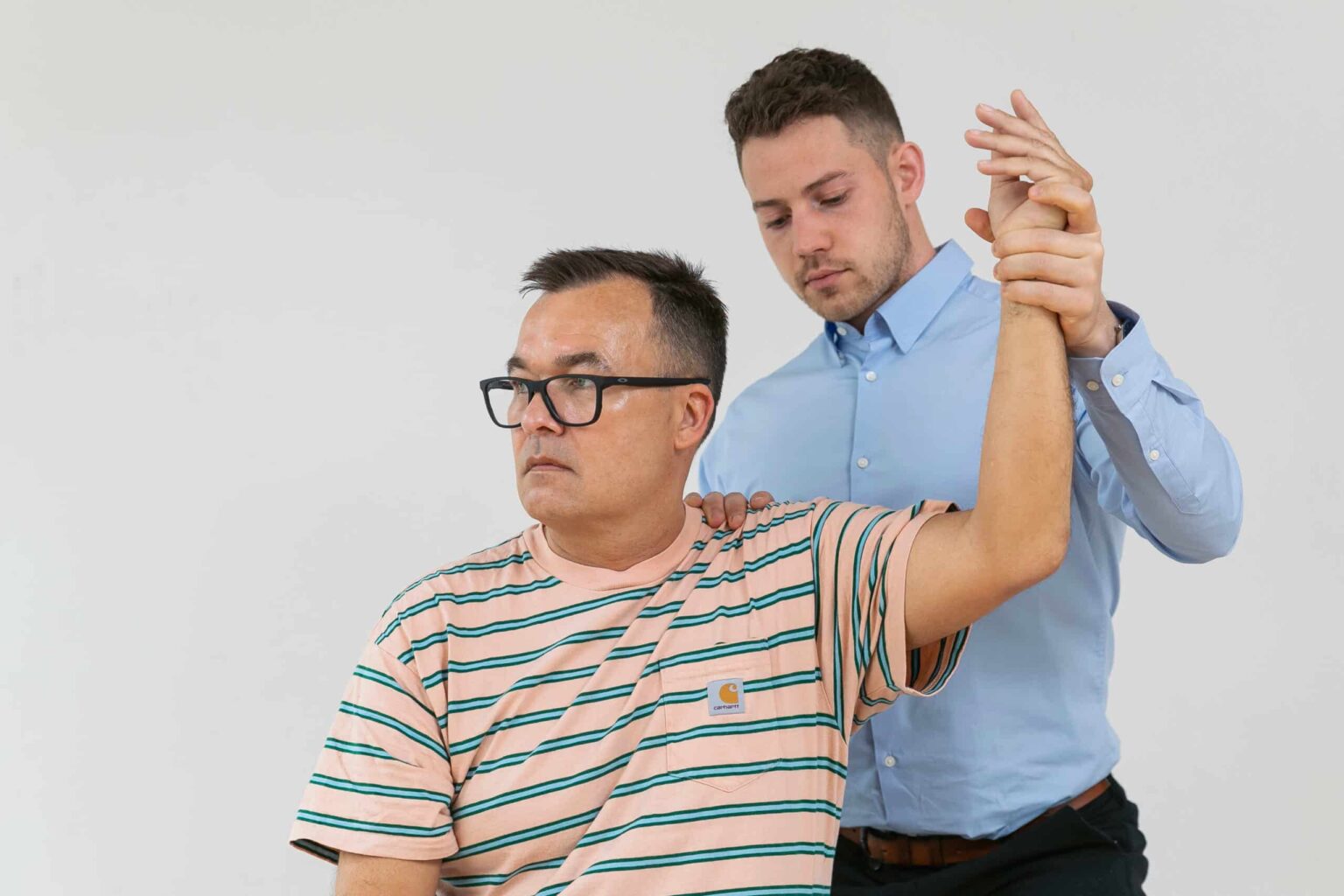

Golfer’s Elbow
Tennis elbow
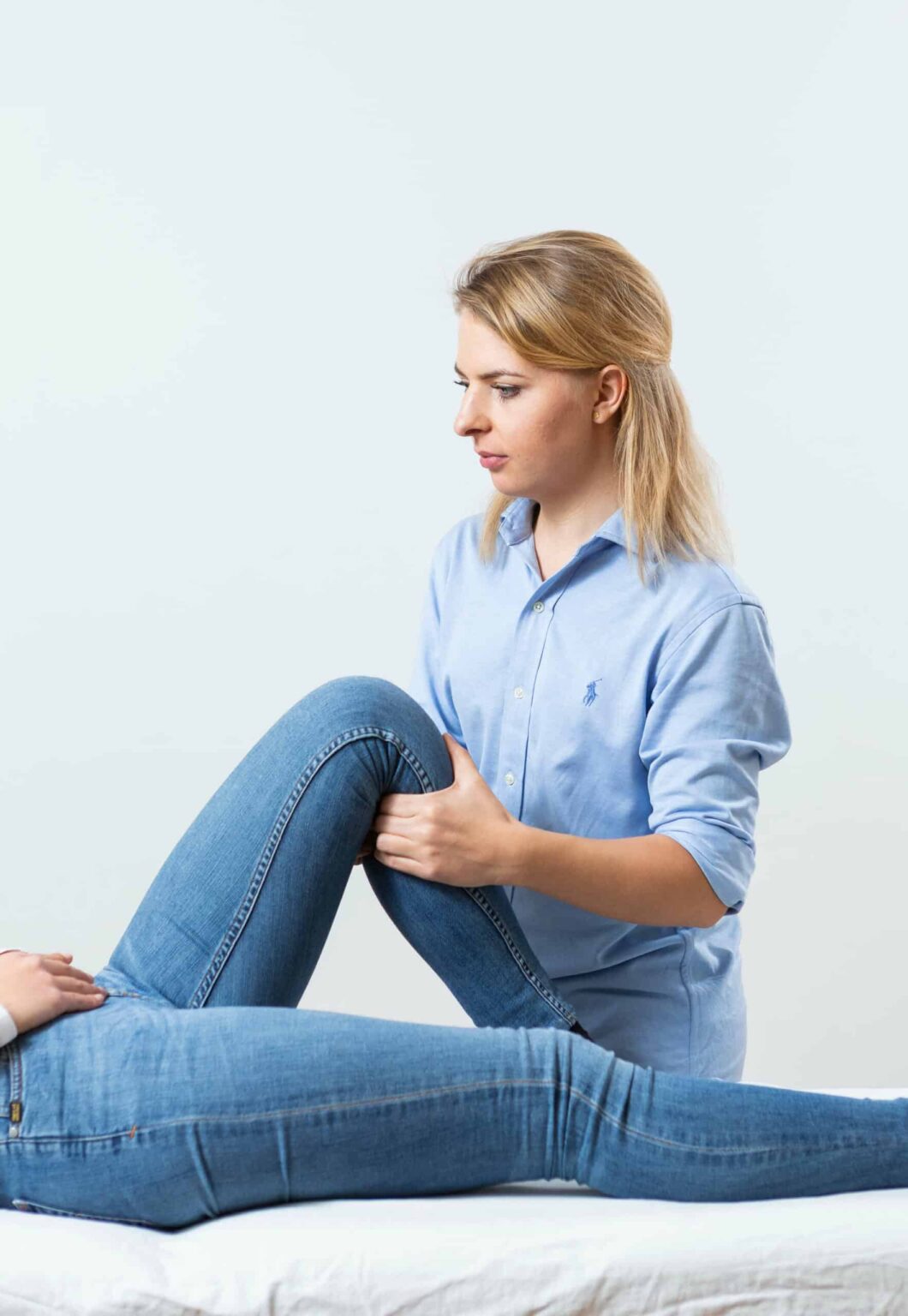

Runner’s knee
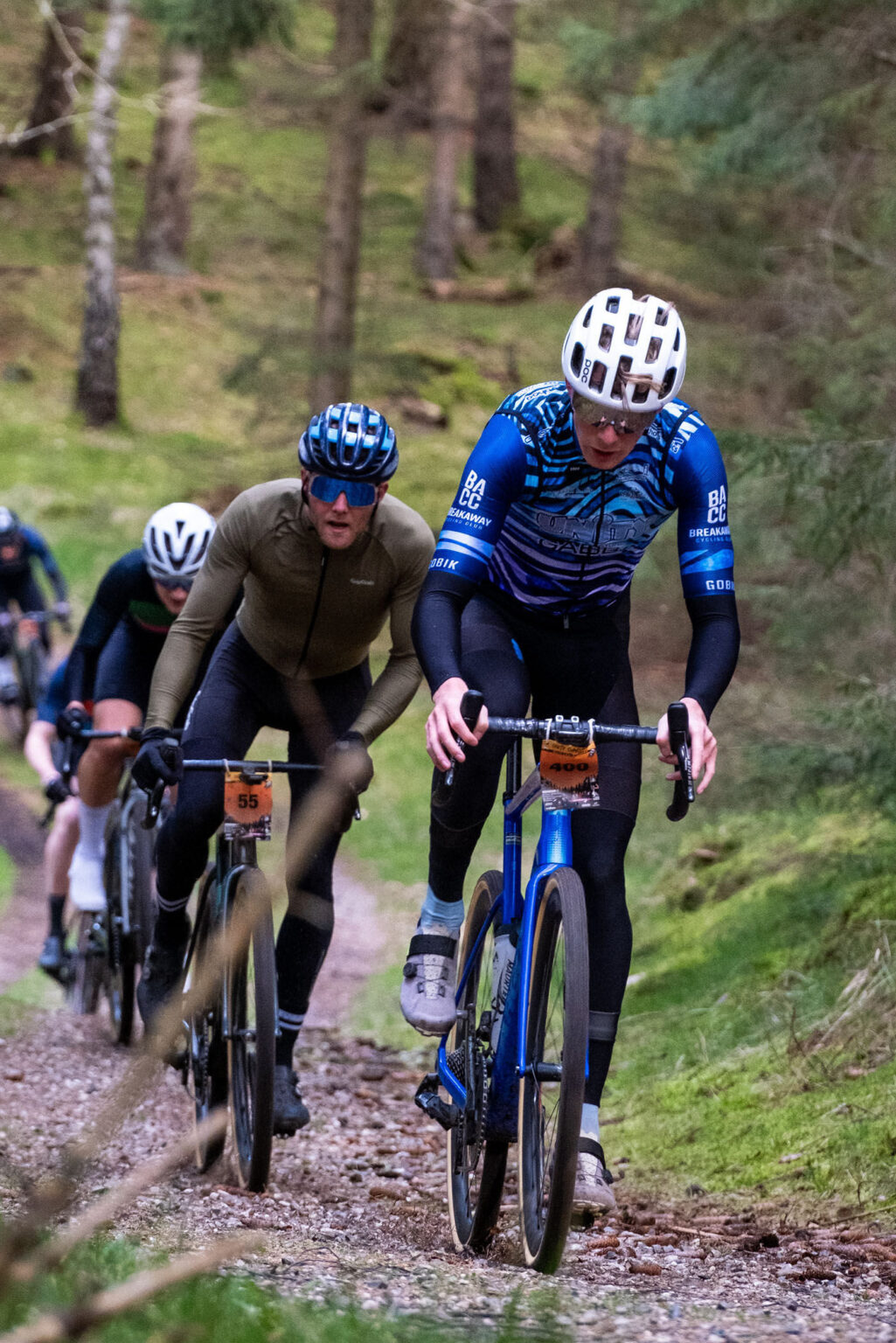

Bicycle injuries
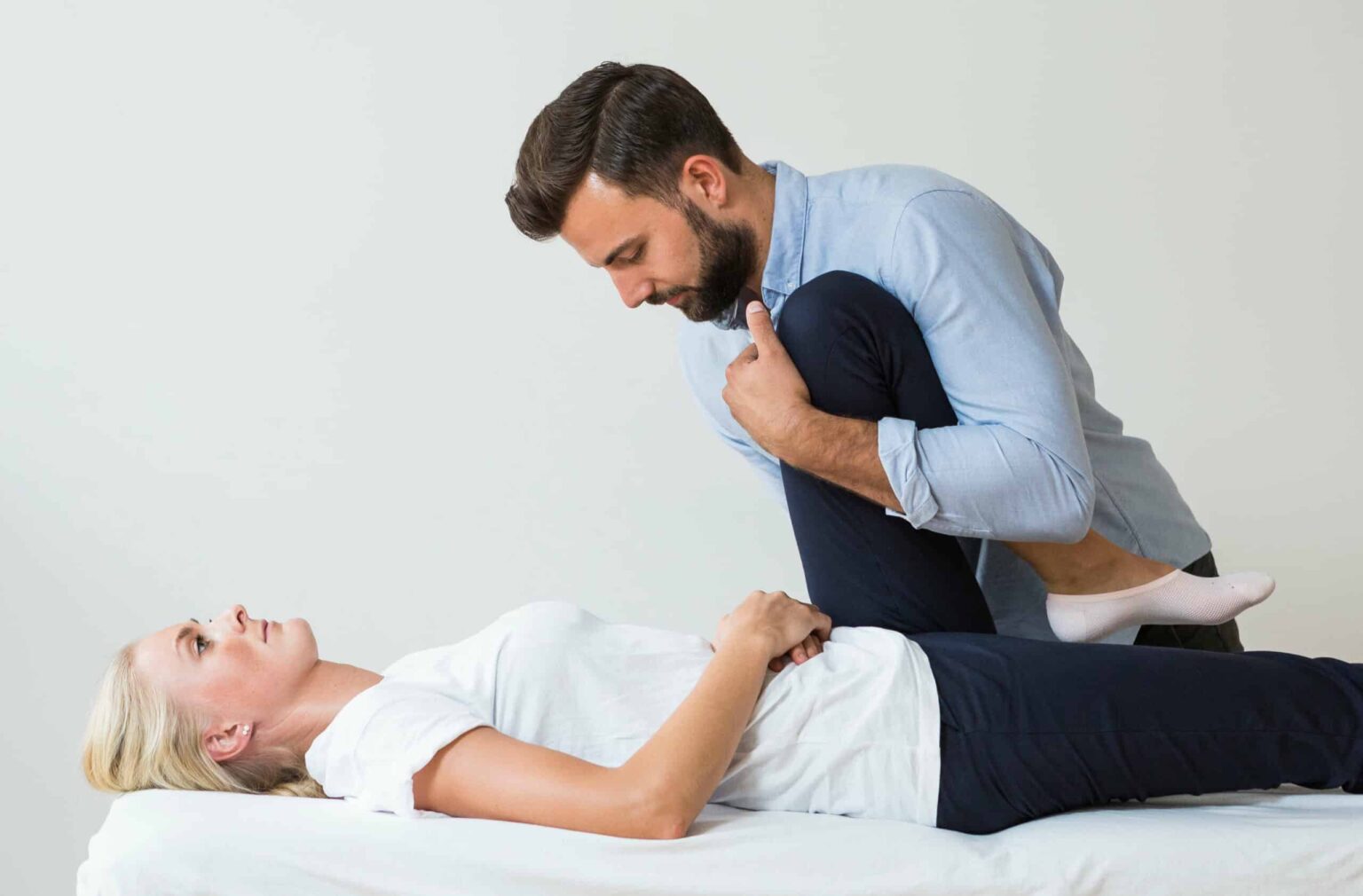

Running injuries

