We treat
Constipation in babies
Learn more about baby constipation on this subpage
What is constipation in babies?
Constipation can be described as hard stools (sluggish stools), stools that are difficult to pass and/or where there is a long time between stools (infrequent stools). With constipation, the stool will become harder and firmer, which will make it difficult for the child to push the stool out and will therefore be bothered by it.
Jump to section [Show]
Symptoms of stomach pain and constipation in babies
The classic symptoms are abdominal pain, crying spells, baby colic, painful stools that are hard lumpy or thin. Constipation is assessed based on stool frequency and stool appearance combined with crying spells, painful stools where the child pushes without anything coming out.
In many cases, it can take days and in rare cases weeks before the child is able to have a bowel movement. However, it is important to emphasize that constipation is not dangerous.
Diagnosing constipation in babies by your doctor
Functional constipation (Rome IV criteria). Two or more of the following criteria must be met in a child, at least once a week for 1 month prior to diagnosis:
- 2 or fewer bowel movements per week in a child with developmental milestones of 4 years or older
- At least one episode of fecal incontinence per week
- History of retentive behavior or extreme voluntary retention of stool
- History of painful or hard stools
- Presence of major fecal impaction in the rectum
- History of passing large amounts of stool
- After relevant investigation, the symptoms cannot be explained unambiguously based on other medical differential diagnoses.
Source: Sundhedsstyrelsen

Causes of constipation in babies
Babies and children often suffer from constipation in the first months or years of their lives. A baby’s digestive system does not secrete sufficient amounts of digestive enzymes until 6-9 months of age, which is why the gastrointestinal system can be sensitive at times.
Neck and back problems that arise during difficult labor can worsen and prolong this period if left untreated.
Physiologically, it is the large intestine that is responsible for shaping and delivering stool to the rectum. Various problems with the large intestine and/or the digestive system’s control can influence the development of constipation. The duration of constipation can also vary individually.
How long can it take for babies to have a bowel movement?
Breastfed babies typically have daily bowel movements or once a week. Breastfed babies do not need to have a bowel movement every day. If your baby is bottle-fed with formula, they should have a bowel movement daily.
Stomach ache baby and infants
The big disadvantage of the child experiencing stomach pain, stomach cramps and stomach ache is that over time the child will unconsciously hold back their stool, which makes the stool stay longer in the colon. This increases the absorption of water from the stool, making it even harder. This can cause the child to remain constipated.
A constipated infant often has colic pain (also called “immature bowels”) because the large amount of stool in the intestine forces the intestine to expand.
Breastfeeding and constipation in infants
There is a difference between breastfeeding your child or giving your child a bottle.
A breastfed baby does not get constipated quite as often. This is because breast milk is easy to digest. Breastfed babies have more beneficial bacteria in their colon, which are able to break down some of the proteins in the milk that are otherwise difficult to digest. This means that the stool becomes softer, and it is therefore easier for the baby to empty its bowels.
Breastfed babies also have higher amounts of motilin, a hormone that stimulates bowel movements.
The composition of breast milk changes as the baby grows and therefore breast milk meets all the needs of the infant during the breastfeeding period.

Infant formula and baby constipation
A bottle-fed baby is more likely to be constipated because formula can be more difficult for the baby to digest. An infant who is only fed formula usually has fewer bowel movements than a breastfed baby. The stools become thicker and may have a different, greener color.
Medical treatment of baby and infant constipation
In case of severe constipation, in consultation with your doctor, you can use movicol or lactulose. In some cases, drops that stimulate intestinal peristalsis, such as laxoberal, can also be used.
Good advice against constipation in babies and infants
There are several treatments for constipation and you can do a lot yourself.
A good tip is to give the child fluids in the form of water. In addition, there are several treatment methods that are often very successful for the child.
What you can do yourself is:
- Massage the child’s stomach in a clockwise direction, possibly with oil or cream, several times a day.
- Cycling movements with your legs, for example, every time you change your child’s clothes. Remember to do the exercises at a calm pace so that the child feels safe and relaxed.
- Give the child a warm bath, which can also help the child relax and thereby make the stool easier to pass.
- You can try to stimulate the anus by using a cotton swab. It is very much about creating a calm environment around the child, so that we stimulate the calming hormones that are used to get rid of stool.
- It is a good idea to start on porridge, fruit or vegetable purees when the baby is 4 months old to provide more fiber to the intestines and thereby prevent constipation. Prunes are particularly useful for this purpose.
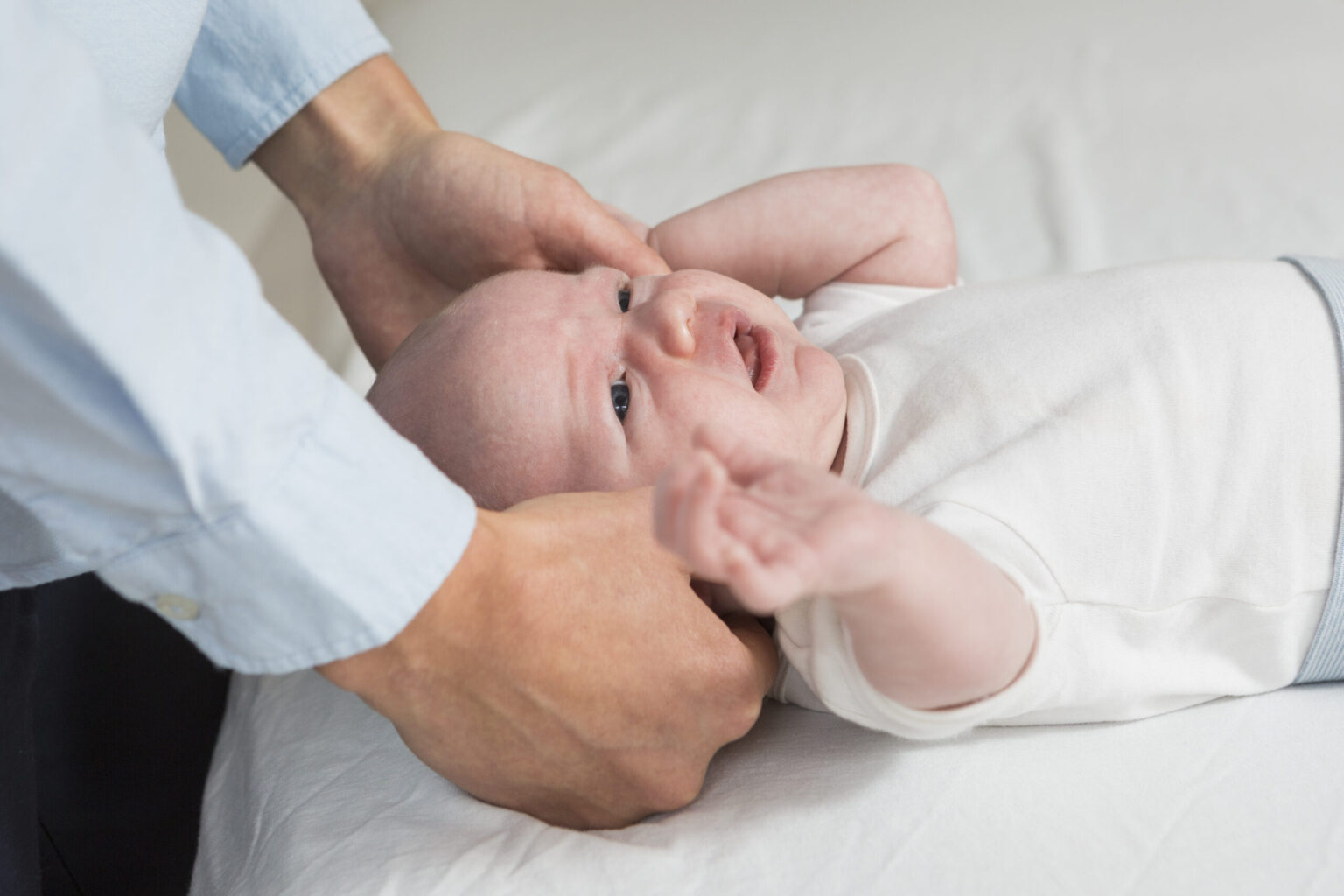
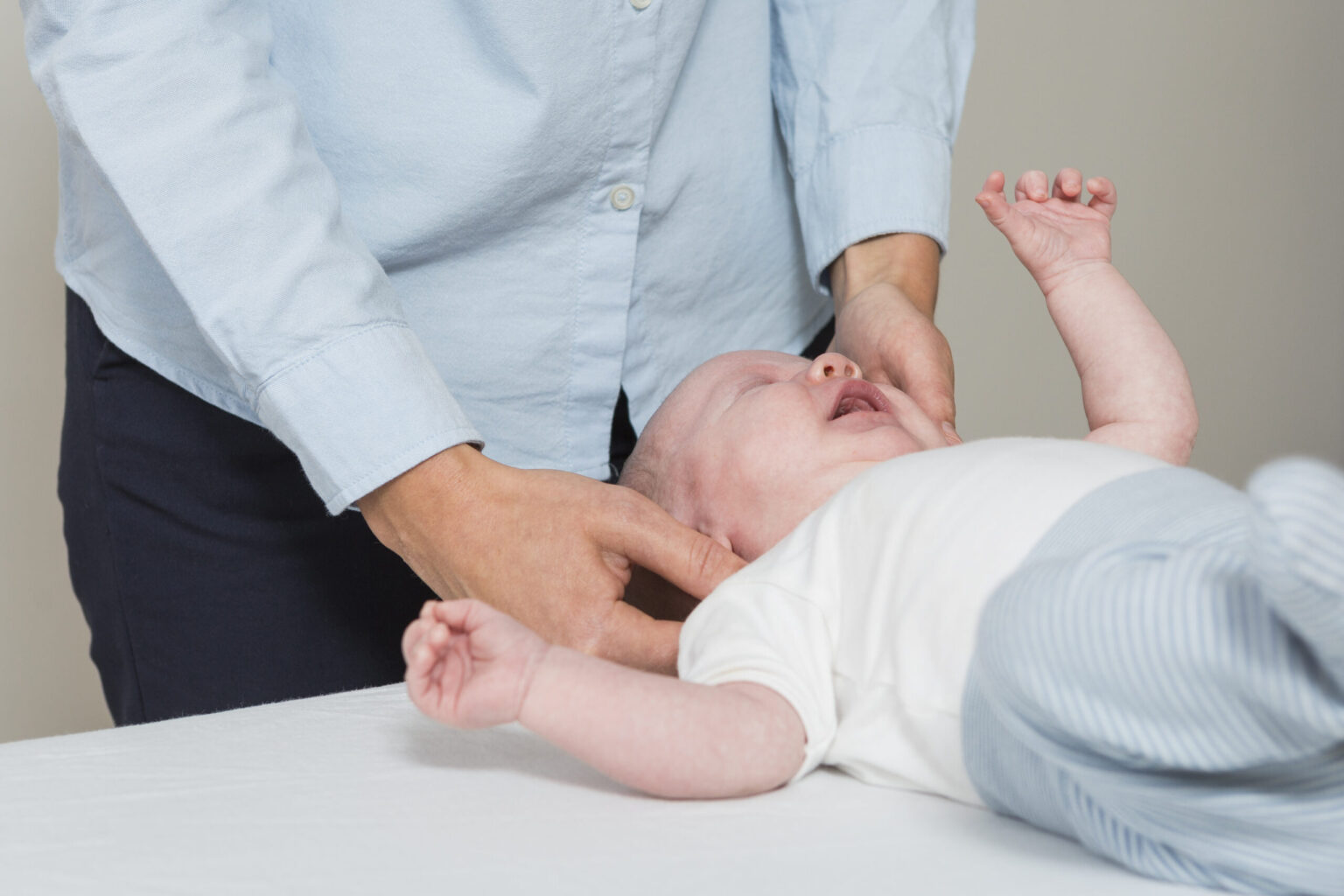
Osteopathic treatment of baby constipation
Osteopathic treatment of constipation will primarily include treatment of the neck and skull to release restrictions around the vagus nerve.
We always strive to use gentle techniques when treating babies and you will often be given exercises, good advice and/or other things to take home with you to help relieve your child’s constipation as quickly as possible.
In addition, the body’s autonomic nervous system (sympathetic and parasystemic nervous systems) is treated, treatment of all parts of the gastrointestinal system to make the movement of the intestinal system more free, and treatment of selected places in the musculoskeletal system that are related to digestion, such as the diaphragm where the stomach is located, and the pelvis where connective tissue from the colon and rectum is attached.

Often related problems

Hypermobility in babies and children

Muscle tension or imbalances in babies and children

Torticollis

Colic-Like Behaviour in babies

Tongue-Tie and Feeding Challenges in Babies

Baby treatment
Scoliosis

