We treat
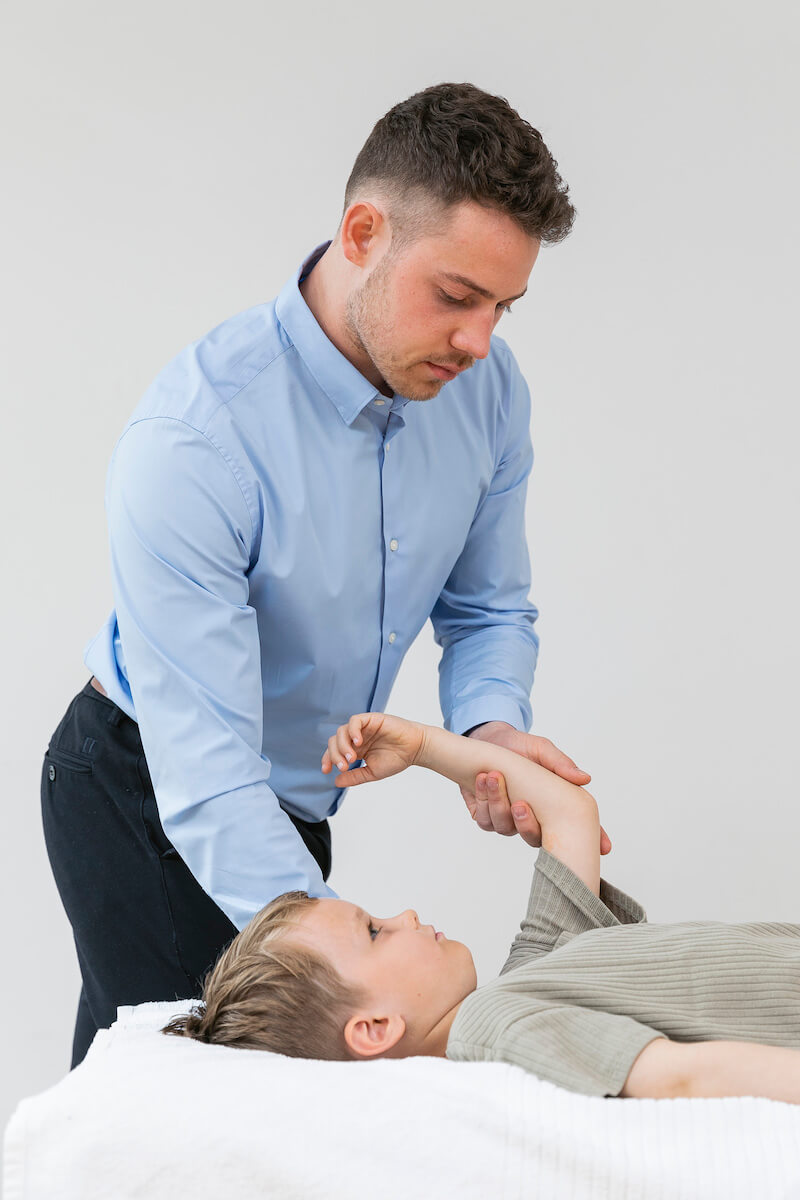
Elbow and wrist pain
Learn more about elbow pain and wrist pain
Elbow and wrist pain
Injuries to the elbow, forearm and wrist are unfortunately quite common. It is thought to affect around 3% of the population. These injuries are also quite difficult to get rid of as most people use their elbow, arm and forearm extensively in connection with, for example, office work.
Jump to section [Show]
Types of elbow injuries
There are many types of injuries/pain in the elbow, hand and forearm.
Here are the most common elbow injuries:
Tennis elbow (lateral epicondylitis)
Tennis elbow is an inflammation of the tendon that attaches to the outside of the elbow. The pain is strain-related, meaning when the muscles that attach to the outside of the arm are in use. The pain can be provoked by, for example, lifting with an outstretched arm or by pressure on the outside of the elbow.
Golfer’s elbow (medial epicondylitis)
Golfer’s elbow is similar to tennis elbow the difference being that with golfer’s elbow pain will be felt on the inside of the elbow
Mouse arm
Mouse arm is not a current diagnosis but a term for pain, excessive tension or other discomfort in the elbow, forearm and/or hand.

Causes of elbow pain (elbow pain)
-
- Mechanical causes: Pain in the elbow itself can originate from the hand, shoulder and chest, as the connective tissue and muscles related to the elbow usually originate there. Posture and/or reduced mobility in these areas are often the cause of elbow pain.
-
- Neurological causes: The nerves that supply all structures in the elbow come from the neck and back. Therefore, neck pain and back pain can be the cause of dysfunction in the nervous system in the elbow.
-
- Vascular (blood circulation) causes: Optimal blood supply to and from the injured area is essential for the body to heal the problem. Therefore, all areas that influence blood supply, i.e. the chest, back, shoulder, upper arm, etc. are very important to examine.
-
- Physiological causes: Certain conditions in the body, such as improper acidity and too much glucose (too much sugar intake), can make it easier for inflammation to occur. Here, diet and organ systems are the cause of chronic (persistent) elbow pain.
Source: Sundhed.dk
Hand pain (hand injuries)
-
- Carpal tunnel syndrome: can be divided into three different types of tendinitis 1. (inflammation of the tendon sheath in the wrist), 2. (inflammation of the membrane around the tendons in the forearm or hand), and 3. (inflammation of the inside of the tendons in the forearm or hand). Women in menopause and people who work with vibrating instruments are often affected by carpal tunnel syndrome.
-
- Trauma: A fall or blow to the hand can cause a minor fracture and/or misalignment of the carpal or forearm bones, which can cause a lot of discomfort for a long time.
-
- Arthritis or osteoarthritis: Worn out cartilage and/or arthritis in the joint is an often overlooked phenomenon. These conditions can cause periodic attacks that are often very painful.
The causes can be mechanical, neurological, vascular and physiological, as in the case of elbow pain.

Osteopathic approach elbow and wrist pain
We are experts in manual diagnosis and treatment of elbow and hand pain. We examine all systems in the body to find the cause(s) of elbow/hand pain.
Elbow and wrist pain often requires physiotherapy rehabilitation (physiotherapist specializing in elbow and wrist) to strengthen and stabilize muscles and connective tissue.

Often related problems
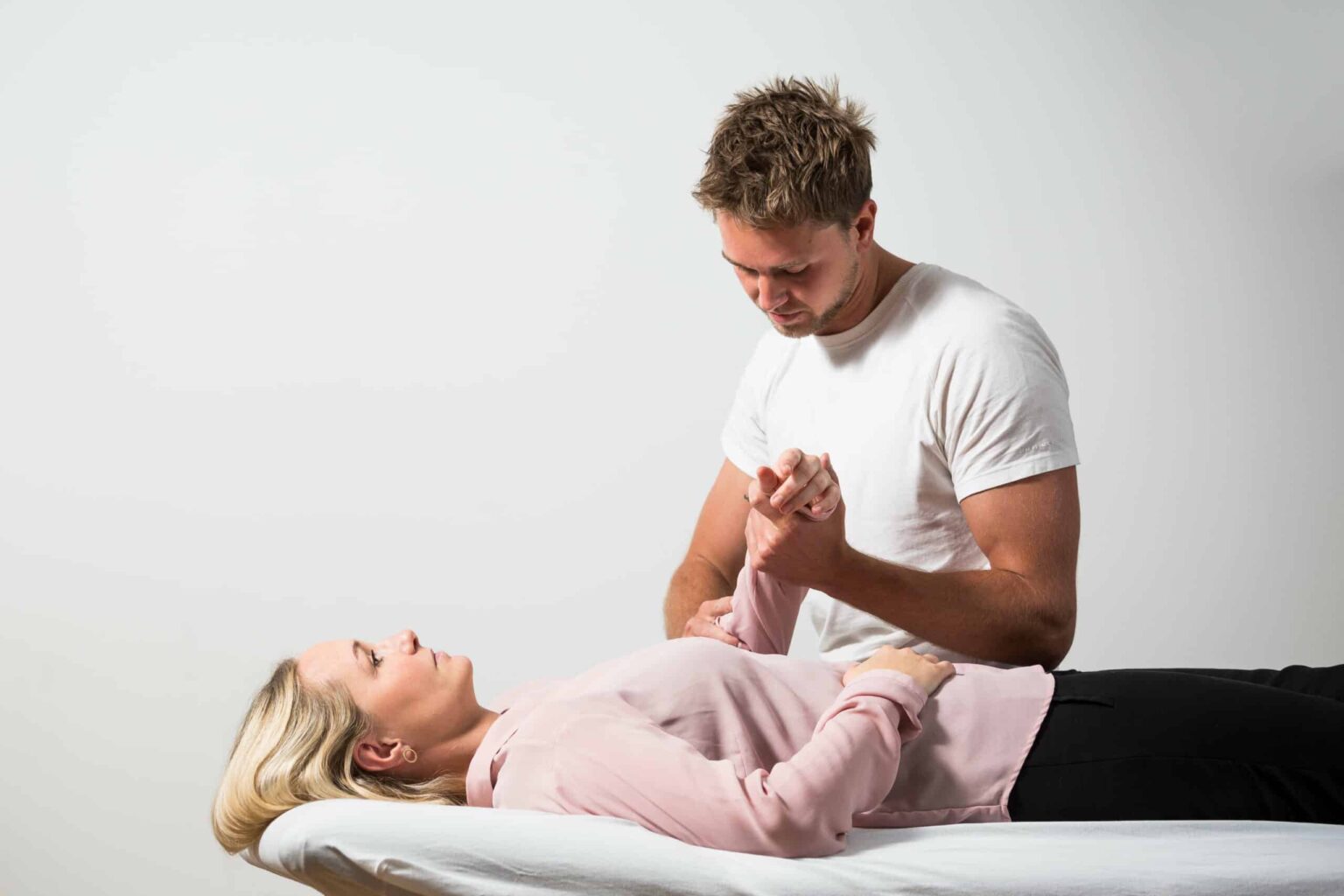

Trigger finger
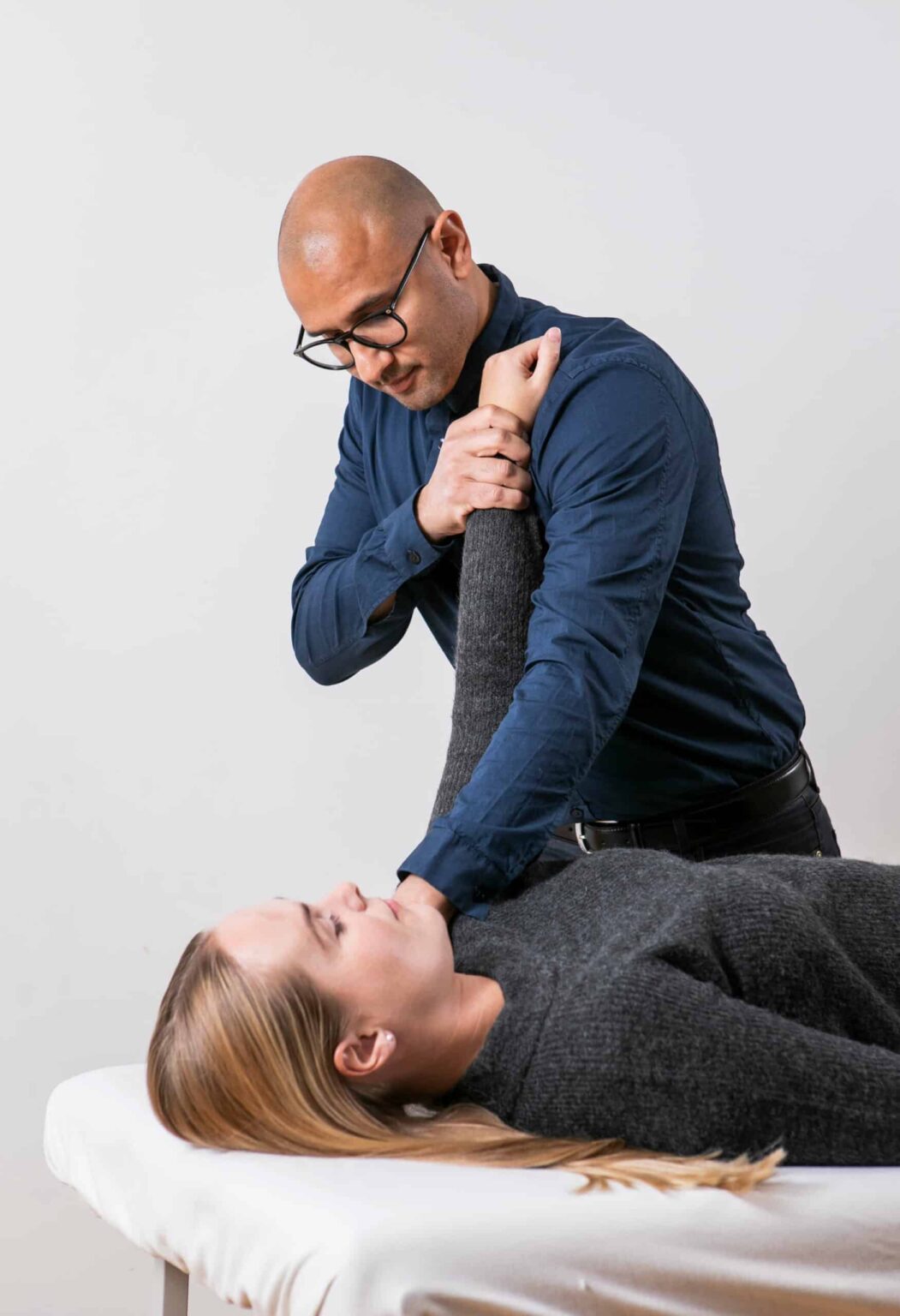

Carpal tunnel syndrome

Tenosynovitis
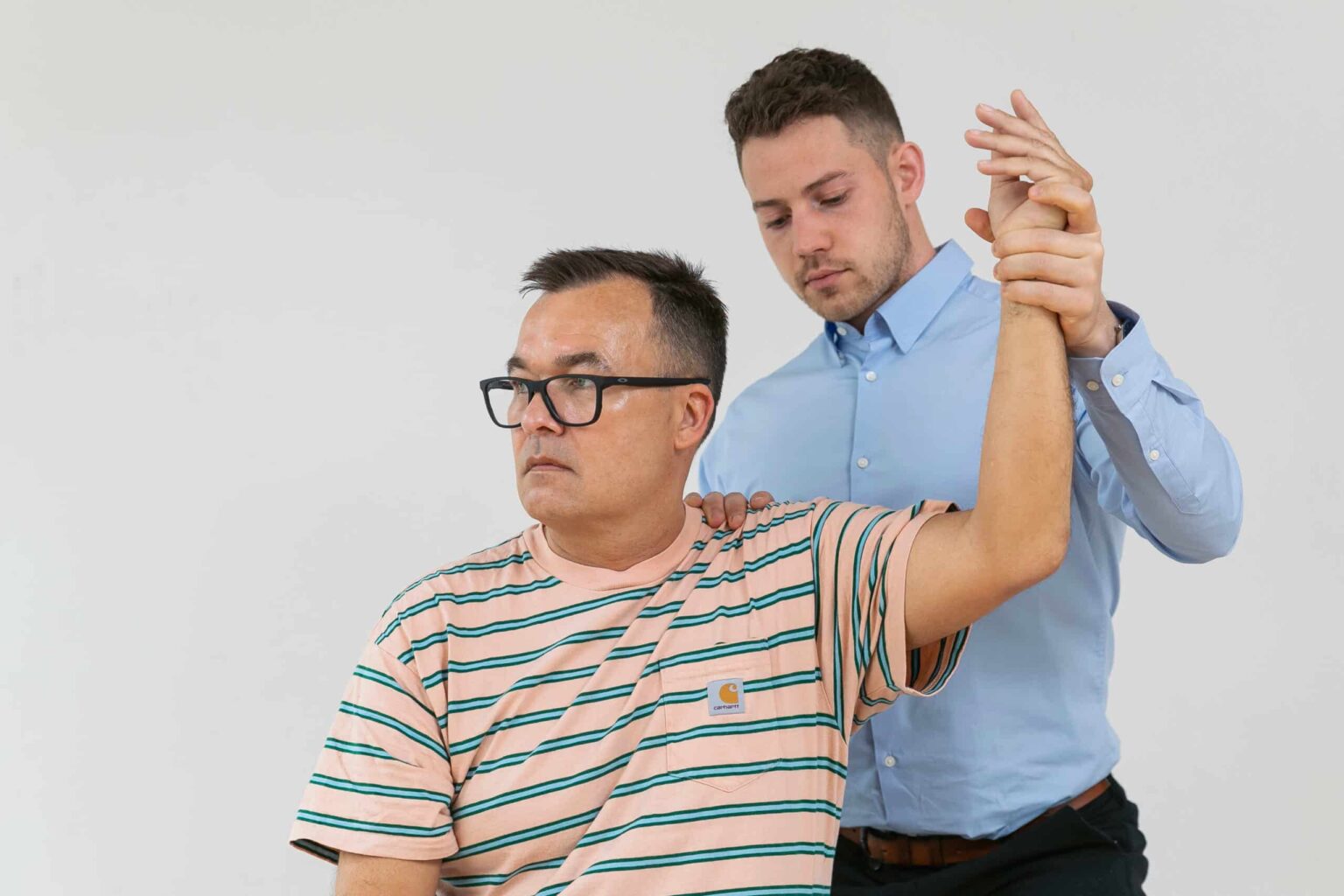

Golfer’s Elbow
Tennis elbow

