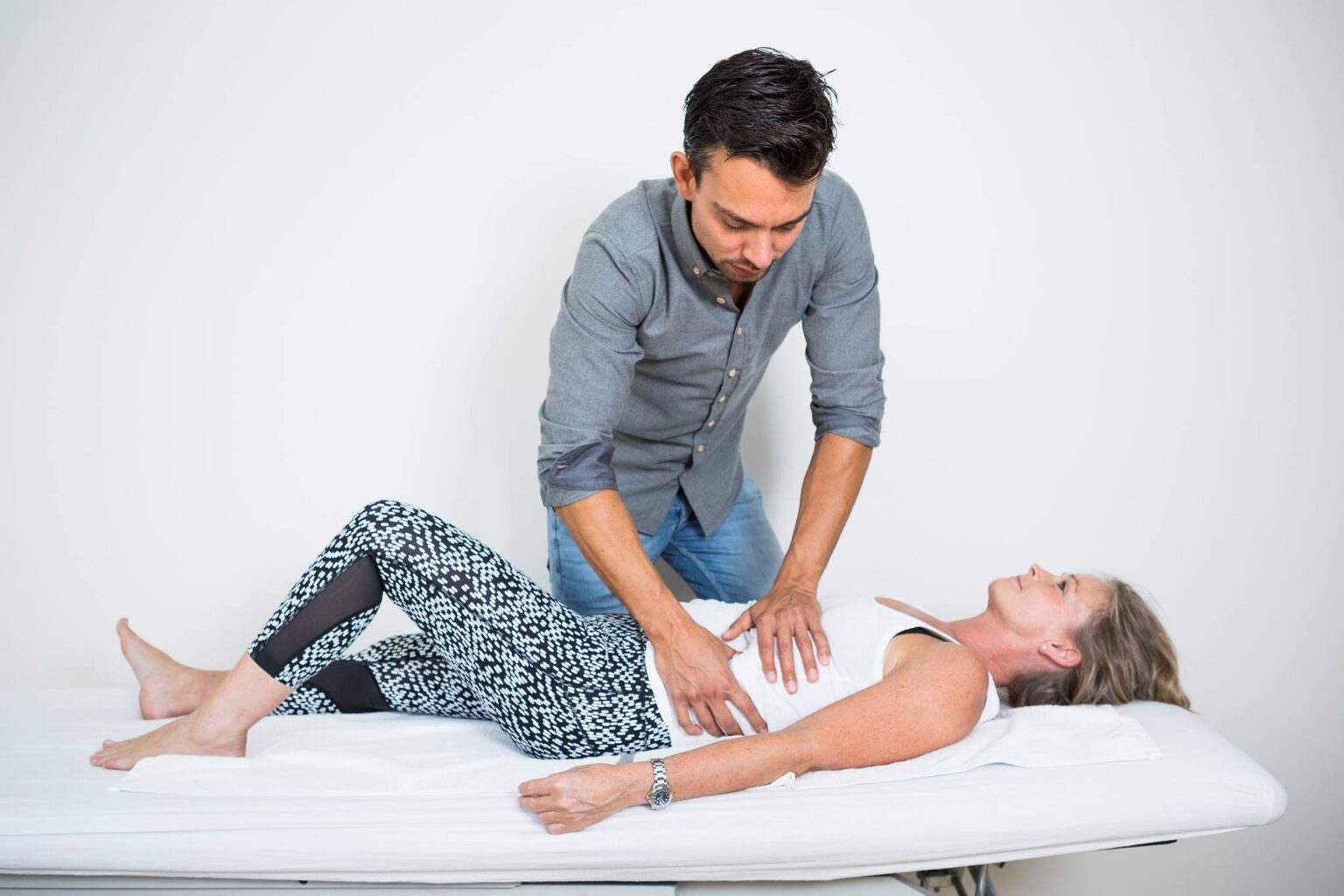
We treat discomfort from
Ovarian surgery
Learn more about ovarian surgery (removal of ovaries) here
What is ovarian surgery?
Ovarian surgery is performed to diagnose or treat various conditions of the ovaries. This may include removal of cysts, endometriosis, or tumors, as well as blockage and repair of the ovaries. Ovarian surgery can be performed using various methods, including laparoscopy or open surgery, depending on the specific condition and the patient’s health.
Before the surgery, the patient will be carefully assessed by the doctor to ensure that she is suitable for surgery and to determine the best approach to the procedure. The woman will receive information about the procedure and fasting rules before the surgery, as well as information about possible interruptions of certain types of medication.
Jump to section [Show]
Ovariectomy (removal of the ovary) – everything you need to know
When performing an ovariectomy, this will usually be done through a laparoscopic operation. In some cases, the surgeon may choose to perform the procedure through open surgery if there are circumstances that warrant this.
During laparoscopic surgery, a scope is inserted through a small incision at the navel. The abdominal cavity is filled with air so that the doctor can get an overview of the abdomen. Two small incisions are made in the bikini line where auxiliary instruments can be inserted.
In open surgery, only the diseased tissue/organ is usually removed in the case of benign conditions. In the case of malignant tumors, it will often be necessary to remove both ovaries, uterus, fatty tissue and appendix due to the risk of spread to these organs. This is agreed with the doctor before the operation.
If part or all of one ovary has been removed during surgery, it does not affect your hormone production, as the other ovary can fully take over production. In cases where both ovaries have been removed, hormone therapy is necessary if you have not passed menopause.
(Source: Region Midtjylland)

Postoperative care after ovary removal
After an ovary removal, it is important to follow the recommended post-operative care to promote the healing process and minimize the risk of complications. Below are some general guidelines to help ensure a good healing process:
1. Pain relief: Medications will be prescribed to relieve pain and discomfort after surgery. These medications should be taken as directed by the doctor.
2. Activity: It is generally recommended to avoid heavy lifting and strenuous activities for some time after surgery. It is important to rest and give the body time to recover. Gradually increased activity can begin as your doctor allows.
3. Wound care and observation: Follow your doctor’s instructions regarding wound care. Any bandages or plasters should be changed as directed. Also, monitor the wound for signs of infection, such as redness, swelling, or drainage – if an infection is suspected, your doctor should be contacted.
5. Follow a healthy diet: A healthy diet with plenty of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains is important to promote the healing process.
6. Shoulder pain: It is common to experience shoulder pain after a hysterectomy due to the gas used during the surgery. It may help to lie down, rest, and apply heat or cold to the shoulders to relieve the pain.
7. Follow-up: Follow up at agreed times with the treating physician to ensure that healing is progressing as expected.
The norm is that you return home from the hospital the same day as your surgery. It is agreed whether you will come to the hospital for a check-up or be called by a nurse. It is also agreed how you will get the results of the examination of the tissue removed during surgery.
You will probably be more tired than usual for several weeks after the operation. You can expect to be on sick leave for 2 weeks after the operation, and for 3 weeks if you have a heavier workload.
Hormone replacement therapy after ovarian surgery
After ovarian surgery, hormone replacement therapy may be an option to replace the hormones that the ovaries no longer produce.
Hormone replacement therapy (HRT) involves taking hormones such as estrogen and progesterone to maintain hormonal balance in the body.
HRT may be necessary if a woman experiences symptoms of hormone deficiency after ovarian surgery, such as hot flashes, vaginal dryness, sleep disturbances, or mood swings. HRT may also be necessary to maintain general health, including bone strength and heart health.
However, it is important to know that HRT can have side effects and risks, including an increased risk of certain cancers and cardiovascular disease. Therefore, treatment should be carefully weighed against its benefits and risks, and regular follow-up visits with your doctor are important to monitor any changes in your body.
Hormone replacement therapy can be taken as pills, patches, creams, vaginal rings, or injections, depending on preferences and individual needs. Dosage and duration of treatment will also vary depending on the individual patient.
(Source: Copenhagen Cardiovascular Clinic)

Gynecological surgery – ovary removal
Gynecological surgery can seem scary and overwhelming to many women, and one of the procedures that often raises concerns is ovarian removal – but it doesn’t have to be as complicated as it sounds.
Ovariectomy – also known as ovariectomy – is a surgical procedure in which one or both ovaries are removed. There may be several reasons for performing this surgery as mentioned in Section 1, including treatment of tumors, endometriosis, ovarian cysts, or as a preventive measure against cancer.
It is important to remember that ovarian removal is a safe and effective procedure that can help women address a variety of health issues. By understanding the procedures and knowing what to expect, patients can reduce their fears and be able to make informed choices about their health.
(Source: Sundhed.dk)
Risks of ovarian removal
The risks of ovarian removal during surgery are small – bleeding and infection are among the most common complications. However, in rare cases, surrounding organs can be damaged. This can include the bladder, urinary tract, intestines or blood vessels.
The injury will be treated during the same surgery as far as possible. However, it may be necessary to change the surgery to an open surgery also called a “bikini incision”, which is a cross-section in the abdominal wall just above the hairline at the pubic bone.
In very rare cases, the complication is only discovered after the operation.
After all operations, inflammation or bleeding can occur, possibly as a hemorrhage inside the body. In rare cases, internal bleeding can develop into a life-threatening condition if it is not detected and treated in time.
Furthermore, there is always a small risk when you are under full anesthesia and therefore you will always be thoroughly assessed by an anesthesiologist before surgery.

Indications for ovariectomy: When is it necessary?
There may be various reasons for removing the ovaries, such as endometriosis, cysts, benign or malignant tumors, or breast cancer. Removing the ovaries may also sometimes be recommended as part of having the uterus removed (hysterectomy).
Health effects of ovarian surgery – what to expect
Ovarian surgery can have different health effects, depending on the reason for the surgery and the type of procedure. Here are some common health effects you can expect after ovarian surgery:
1. Pain and discomfort: After the surgery, you may experience pain and discomfort in the area around your ovaries. This may last for a few days or weeks, depending on the extent of the procedure.
2. Bleeding: Minor bleeding from the wound is normal after surgery. However, this should stop within a few days. If the bleeding becomes heavy or lasts for a long time, contact your doctor.
3. Scar tissue: Ovarian surgery can leave scar tissue that can affect ovarian function and cause pain or discomfort later on. If you experience persistent symptoms, see a doctor.
4. Infection: Any type of surgical procedure increases the risk of infection. It is important to follow your doctors’ instructions on wound care and take any antibiotics prescribed to reduce the risk of infection.
5. Hormonal changes: Depending on the type of surgery, ovarian surgery can affect your hormone levels. This can cause changes in your menstrual cycle, mood swings, or other hormone-related symptoms. These changes can be temporary or permanent, depending on the extent of the surgery.
6. Fertility: If you have ovarian surgery on one or both ovaries, this may affect your fertility. If you are planning to become pregnant in the future, it is important to discuss this with your doctor, as some types of surgery may reduce your ability to conceive naturally. There may be alternative methods such as fertility treatment or ovarian transplantation that can be considered.
(Source: Breastcancer.org)

Quality of life after removal of ovaries
Removing the ovaries can have different consequences for quality of life, as it depends on several factors such as age, hormonal status and any underlying diseases.
For women who have both ovaries removed before menopause, it will result in an acute menopause, which can have a significant impact on quality of life. This is due to the drop in estrogen levels, which can cause symptoms such as hot flashes, sleep disturbances, mood swings, decreased libido, and dry mucous membranes. These symptoms can have a negative impact on physical, emotional, and sexual well-being. If the woman has not already gone through natural menopause before the surgery, it can be particularly challenging to cope with a sudden and significant drop in hormone levels.
In addition, removing the ovaries may also increase the risk of certain long-term health problems, such as cardiovascular disease and osteoporosis (brittle bones). These risks can also affect quality of life.
It is important to note that many women maintain a good quality of life after removal of the ovaries.
There are various treatment options available to relieve the symptoms of menopause, including hormone replacement therapy (HRT) and lifestyle changes. Women should consult with their doctor to evaluate the best options for maintaining or improving their quality of life after removal of the ovaries.
Long-term consequences of ovariectomy
After an ovariectomy, there may be several long-term consequences that a person must navigate and deal with. Some of these consequences include:
1. Hormonal changes: The ovaries are responsible for the production of several hormones, including estrogen and progesterone. When the ovaries are removed, the levels of these hormones can drop significantly. This can lead to various symptoms such as hot flashes, vaginal dryness, mood swings, and decreased libido. Navigating these hormonal changes may require hormone replacement therapy or other forms of treatment.
2. Infertility: If a woman wants to preserve her fertility, an ovariectomy may make it impossible to conceive naturally. In some cases, egg transfer or in vitro fertilization (IVF) may be necessary before the surgery to preserve the eggs for later use.
3. Increased risk of certain diseases: With the removal of the ovaries, there may be an increased risk of certain diseases such as osteoporosis and heart disease. It is important to be aware of and take steps to reduce this risk, such as maintaining a healthy lifestyle and taking necessary supplements.
4. Psychological and emotional challenges: An ovariectomy can have a significant impact on a woman’s emotional well-being. Many women may experience a sense of loss or grief over the loss of their ovaries and the ability to have children naturally. It may be helpful to seek support from a therapist or support group to address these emotional challenges.
5. Physical Health and Lifestyle: After an ovariectomy, there may be certain physical health aspects to navigate. This may include pain or discomfort after surgery, maintaining a healthy weight, managing any scars or other surgical complications, and being aware of any breast or body changes.
Adhesions can form between the organs in the abdominal cavity. Adhesions can occur after previous abdominal surgery. Laparoscopic surgery carries a lower risk of adhesions than open surgery.

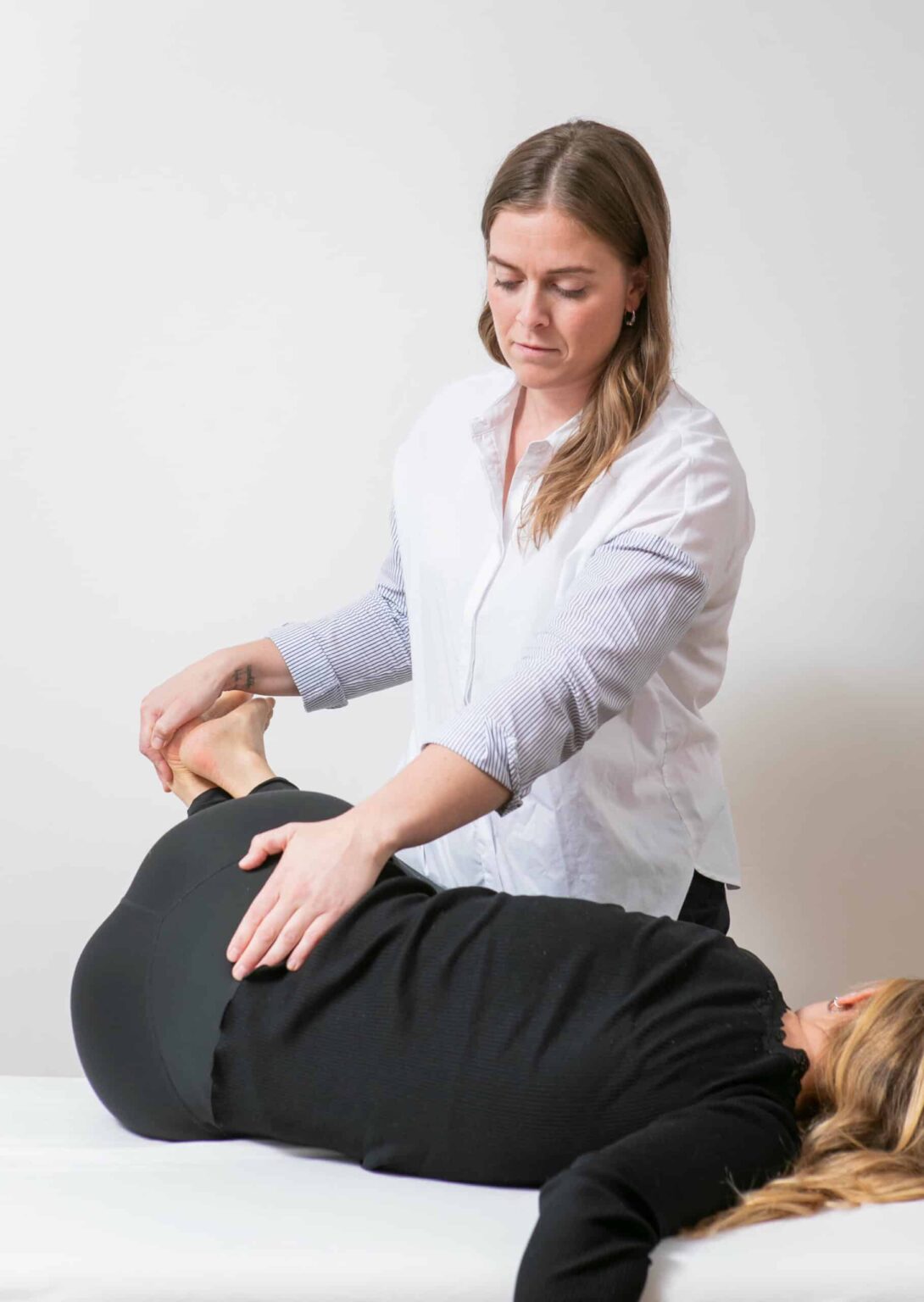
Osteopathy 101: Basic Principles and Methods
Osteopathy is a form of treatment that focuses on the body’s ability to heal itself. Osteopaths use a variety of methods and techniques to restore balance and function to the body.
Osteopathic treatments are based on the following principles:
1. The body is a whole: Osteopaths view the body as a unit where all parts are interdependent. They look at how structural and functional structures in one area can affect other areas of the body.
2. The body’s ability to heal itself: Osteopaths believe in the body’s natural ability to heal itself. Through proper stimulation and correction of the body’s structures, the body can restore good function.
3. Structure and function are interdependent: Osteopaths focus on both the structure and function of the body.
Methods and techniques that osteopaths use are:
- Manipulation and mobilization
- Myofascial techniques, which by stretching connective tissue and applying pressure to muscles, relieve pain and improve movement.
- Visceral techniques: These are techniques that focus on the structures and function of internal organs to improve movement and function throughout the body.
- CranioSacral Therapy: Techniques that focus on the back and skull.
- Exercises and advice: Osteopaths also provide exercises and advice on lifestyle changes to promote health and prevent injuries.
How osteopathy differs from other forms of therapy
Holistic approach
Osteopathy views the body as a whole, with all systems interconnected and influencing each other. Osteopaths examine not only the area where the client is experiencing symptoms, but also look for causes and related problems elsewhere in the body. This is in contrast to more specific therapies that focus only on the area of the symptom.
Manual treatment
Osteopaths primarily use their hands to diagnose and treat clients. This may involve gentle pressure, stretching, or manipulation of muscles, joints, connective tissue, and organs. Other forms of therapy may use tools or machines to perform the treatment.

Uses of osteopathy: pain relief and stronger health
Osteopathy is a holistic approach to health that aims to relieve pain and promote healing by treating and restoring the body’s natural balance and function. This form of treatment is used in a variety of situations and for a range of conditions:
1. Musculoskeletal problems: Osteopathy is particularly effective in relieving pain and improving function in musculoskeletal disorders such as muscle strains, joint and back pain, sports injuries, herniated discs, fibromyalgia, etc. The osteopath will use various manual techniques to work with muscles, joints and connective tissue to relieve pain, improve range of motion and restore normal function.
2. Digestive problems: By manipulating certain areas of the stomach and intestines, osteopathic techniques can promote digestion and relieve symptoms such as bloating, constipation, irritable bowel syndrome, etc. Osteopathy can also benefit people after surgery in the stomach and intestines, as it can help restore normal bowel function and reduce scarring.
3. Respiratory problems: Osteopathy can help relieve symptoms and eliminate the causes of respiratory problems such as asthma, bronchitis, sinusitis, etc. Restoring normal breathing and releasing blockages in the lungs and bronchi are goals of osteopathy in these situations.
4. Stress-related conditions: Osteopathy can help reduce stress levels and relieve symptoms associated with stress such as muscle tension, headaches, sleep problems, etc. By working with the body’s muscles, skeleton, nervous system, and respiratory system, the osteopath can help restore balance and relaxation.
5. Pregnancy and postpartum: Many pregnant women experience pain and discomfort in their muscles, joints and back during pregnancy. Osteopathy can help relieve this pain and improve the body’s ability to adapt to the physical changes of pregnancy. After birth, osteopathy can help restore the body’s normal function and strength after birth.
These are just a few examples of uses of osteopathy. Osteopathy can be beneficial for anyone looking to improve their overall health and well-being, regardless of whether they have specific symptoms or conditions. However, it is important to note that osteopathy does not treat serious medical conditions or emergencies, and it is always best to consult your doctor for appropriate treatment.

Often related pain

Ovarian surgery

Hysterectomy

Endometriosis
Pelvic pain

Menstrual pain

PMS

Involuntary infertility

